Tutorial
These icons indicate there is something to be interacted with. Click it when you see it.
Tutorial
These icons indicate there is something to be interacted with. Click it when you see it.
Tutorial
These icons indicate there is something to be interacted with. Click it when you see it.
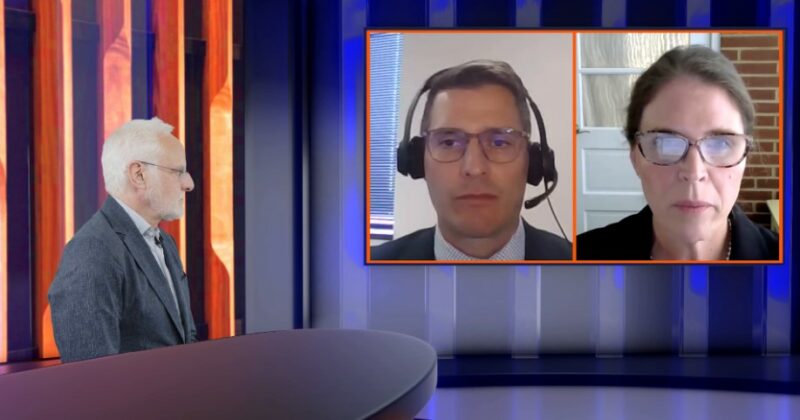
touchPANEL DISCUSSION
 A visually engaging discussion designed to emulate a ‘live’ panel experience and provide clinicians with practical expert insights to address their clinical challenges. Useful tips below will show how to navigate the activity.
Close
A visually engaging discussion designed to emulate a ‘live’ panel experience and provide clinicians with practical expert insights to address their clinical challenges. Useful tips below will show how to navigate the activity.
Close
 A visually engaging discussion designed to emulate a ‘live’ panel experience and provide clinicians with practical expert insights to address their clinical challenges. Useful tips below will show how to navigate the activity.
Close
A visually engaging discussion designed to emulate a ‘live’ panel experience and provide clinicians with practical expert insights to address their clinical challenges. Useful tips below will show how to navigate the activity.
Close
Continuous glucose monitoring in type 2 diabetes: Overcoming barriers to optimize outcomes
Learning Objectives
After watching this activity, participants should be better able to:
- Describe the benefits of CGM in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Apply strategies to overcome barriers to CGM to help increase uptake in patients with type 2 diabetes, including timely referral of eligible patients
- Support patients with type 2 diabetes who are undertaking CGM through effective communication and collaboration with the primary and secondary care teams
Overview
In this activity, three experts provide their perspectives on the benefits of CGM in patients with T2D, strategies to overcome the barriers to its uptake and how to best support patients in implementing CGM. The discussion is guided by questions from HCPs involved in the management of patients with T2D.
This activity is jointly provided by USF Health and touchIME.
Target Audience
This activity has been designed to meet the educational needs of endocrinologists, diabetologists, primary care physicians, pharmacists and diabetes nurse specialists involved in the management of type 2 diabetes.
Disclosures
USF Health adheres to the Standards for Integrity and Independence in Accredited Continuing Education. All individuals in a position to influence content have disclosed to USF Health any financial relationship with an ineligible organization. USF Health has reviewed and mitigated all relevant financial relationships related to the content of the activity. The relevant relationships are listed below. All individuals not listed have no relevant financial relationships.
Faculty
Prof. Stewart Harris discloses: Advisory board or Panel fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer Inc., Dexcom, Eli Lilly and Company, HLS Therapeutics, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi and Applied Therapeutics (relationship terminated).Consultancy fees from Abbott, AstraZeneca, Bayer Inc., Dexcom, Eli Lilly and Company, HLS Therapeutics, Janssen, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi.Grants/Research Support from Abbott, Applied Therapeutics Inc., AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis, Novo Nordisk and Sanofi.
Dr Anders Carlson discloses: Advisory board or Panel fees from MannKind and Novo Nordisk. Grants/research support fees from Abbott, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Insulet, Medtronic, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi and Tandem Diabetes Care.
Prof. Shannon Izdik has no financial interests/relationships or affiliations to disclose in relation to this activity.
Content reviewer
Kaitlyn E Rechenberg, PhD, MPH, APRN has no financial interests/relationships or affiliations in relation to this activity.
Touch Medical Contributors
Sola Neunie has no financial interests/relationships or affiliations in relation to this activity.
USF Health Office of Continuing Professional Development and touchIME staff have no financial interests/relationships or affiliations in relation to this activity.
Requirements for Successful Completion
In order to receive credit for this activity, participants must review the content and complete the post-test and evaluation form. Statements of credit are awarded upon successful completion of the post-test and evaluation form.
If you have questions regarding credit please contact cpdsupport@usf.edu.
Accreditations
Physicians
This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the accreditation requirements and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) through a joint providership of USF Health and touchIME. USF Health is accredited by the ACCME to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
USF Health designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.75 AMA PRA Category 1 CreditTM. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
Advanced Practice Providers
Physician Assistants may claim a maximum of 0.75 Category 1 credits for completing this activity. NCCPA accepts AMA PRA Category 1 CreditTM from organizations accredited by ACCME or a recognized state medical society.
The AANPCP accepts certificates of participation for educational activities approved for AMA PRA Category 1 CreditTM by ACCME-accredited providers. APRNs who participate will receive a certificate of completion commensurate with the extent of their participation.
Pharmacists
USF Health is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education as a provider of continuing pharmacy education. This knowledge-based program has been approved for 0.75 contact hours (0.75 CEUs). Universal program number is as follows: 0230-0000-24-006-H01-P.
Nurses
USF Health is accredited as a provider of nursing continuing professional development by the American Nurses Credentialing Center’s Commission on Accreditation.
A maximum of 0.75 contact hour(s) may be earned by learners who successfully complete this continuing professional development activity. USF Health, the accredited provider, acknowledges touchIME as the joint provider in the planning and execution of this CNE activity.
This activity is awarded 0.75 ANCC pharmacotherapeutic contact hour.
EBAC® Accreditation
touchIME is an EBAC® accredited provider since 2023.
This programme is accredited by the European Board for Accreditation of Continuing Education for Health Professionals (EBAC®) for 0.75 hours of effective education time.
The Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME®), and the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada hold an agreement on mutual recognition on substantive equivalency of accreditation systems with EBAC®.
Through an agreement between the European Board for Accreditation of Continuing Education for Health Professionals and the American Medical Association (AMA), physicians may convert EBAC® CE credits to AMA PRA Category 1 CreditsTM. Information on the process to convert EBAC® credit to AMA credit can be found on the AMA website. Other healthcare professionals may obtain from the AMA a certificate of having participated in an activity eligible for conversion of credit to AMA PRA Category 1 CreditTM.
Faculty Disclosure Statement / Conflict of Interest Policy
In compliance with EBAC® guidelines, all speakers/ chairpersons participating in this programme have disclosed or indicated potential conflicts of interest which might cause a bias in the presentations. The Organizing Committee/Course Director is responsible for ensuring that all potential conflicts of interest relevant to the event have been mitigated and declared to the audience prior to the CME activities.
Requirements for Successful Completion
Certificates of Completion may be awarded upon successful completion of the post-test and evaluation form. If you have completed one hour or more of effective education through EBAC® accredited CE activities, please contact us at accreditation@touchime.org to receive your EBAC® CE credit certificate. EBAC® grants 1 CE credit for every hour of education completed.
Date of original release: 29 August 2024. Date credits expire: 29 August 2026.
Time to complete: 39 minutes
If you have any questions regarding credit please contact cpdsupport@usf.edu.
If you have any questions regarding the EBAC® credits, please contact accreditation@touchime.org.
To obtain contact hours from this activity, please complete this post-activity test.
Claim CreditYou may also be interested in...

REGISTER NOW FOR FREE ACCESS TO
- 1000+ topical and insightful peer-reviewed journal articles
- 100+ hours of bite-sized congress highlights
- 10 major therapy areas packed with the latest scientific advances
- 150+ specialties offering learn-on-the-go medical education
- + Concise email updates and newsletters so you never miss out

Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a .
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.